So you are new to Linux and you downloaded PuTTY (or some other client), connected to your server and you have no idea what to do now.
I will go through some of the most used commands and post screen shots of what it will look like. Before we start if you want to know more about a command you can run “command –help” and it will show the man page for the specific command.
This post is not meant to be a catch all for each commands this post is just to give you a general understanding of how to perform common tasks in a BASH session.
Using cd: Changing Directories:
Changing directories is very simple, and probably the most common task you will preform in a BASH session.
cd (cd to the user's home directory)
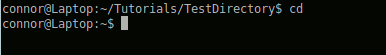
cd directory (change to a directory relative to where your at)

cd /home/connor/directory (change directory relative to the filesystem)

Using ls: Listing Contents:
Another very common task is listing a directory’s contents.
ls (list current directory)
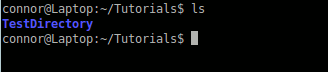
ls directory (list directory relative to where your at)
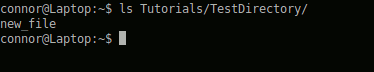
ls /home/connor/directory (list directory relative to the filesystem)
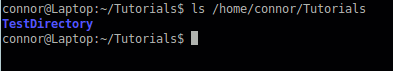
There are options you can add to your “ls” command
ls -a (will list all the files in the directory)
ls -la (will list all the files in the directory in long list format)
Using mkdir: Making Directories:
Okay so you can change directories and list the contents and thats all fine and dandy but what about creating directories? Well yet again this is a simple process.
mkdir (make directory)

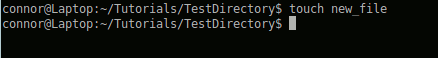
Using touch: Creating Files:
Now you want to create a file inside that directory.
touch (create file)
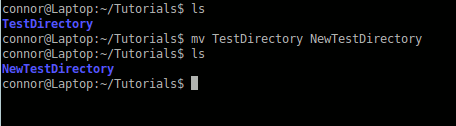
Using mv:
So you want to rename or move a file or directory?
mv (move file / directory)
Using rm:
Now you want to delete or remove a file
Note: This perminantly deletes the file and there is no recycle bin like in Windows!
rm (remove file)
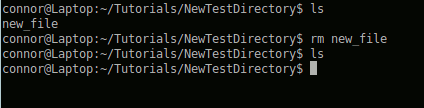
You can not use this method on directories.
rm -r (remove directory)
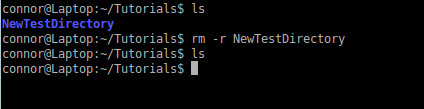
You have to -r the rm command here so that it will recursively remove the contents of the directory.
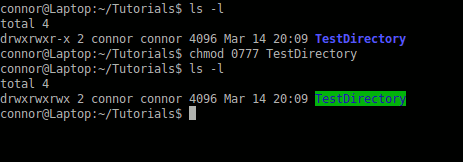
Using chmod:
To change file permissions you need to use a chmod command. I suggest you learn more about file permissions by reading this page before you attempt this command.
Note: I never suggest using 0777 I was just using this as an example.
chmod
Using chown:
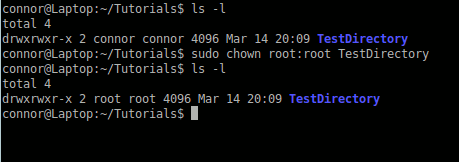
If you want to change ownership of a file or directory you use use the chown command. To chown a file that doesn’t belong to you, you will need to be root (I don’t suggest) or you need to use sudo.
chown
As I stated earlier in this post, this is just a simple overview of some of the most commonly used BASH commands. If you have any questions please comment below or in our forums.








